Cosa sono i fattori ESG
I fattori di tipo ambientale (Environmental), sociale (Social) e di governo societario (Governance) sono quei fattori che vengono generalmente considerati per qualificare un'attività o strumento finanziario come sostenibile.
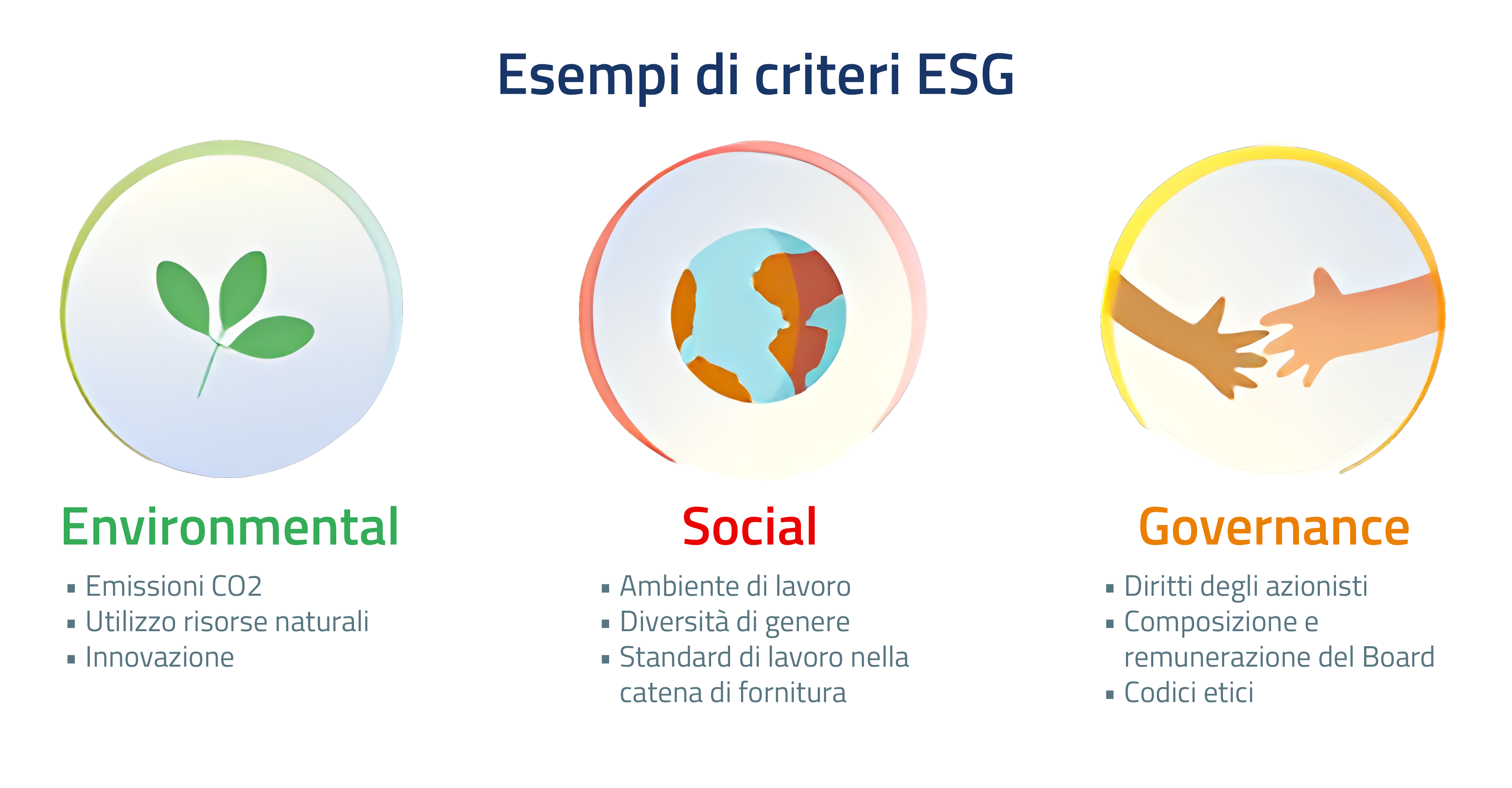
I fattori di tipo ambientale includono questioni come quelle della mitigazione dei cambiamenti climatici e della transizione verso la neutralità climatica, cioè verso un'economia a emissioni nette zero, così come temi relativi alla salvaguardia della biodiversità, alla prevenzione dell'inquinamento e al sostegno all'economia circolare.
I fattori di tipo sociale si riferiscono a questioni relative alle disuguaglianze e all'inclusione, alle relazioni di lavoro, agli investimenti in formazione e al benessere della collettività nonché al rispetto dei diritti umani.
Infine, il governo societario delle istituzioni pubbliche e private ha un ruolo fondamentale nell'assicurare che considerazioni di tipo sociale e ambientale entrino nei loro processi decisionali, ad esempio attraverso le politiche di diversità nella composizione degli organi di amministrazione, la presenza di consiglieri indipendenti o le modalità di remunerazione dei dirigenti.
Fare un investimento finanziario che tenga conto dei fattori ESG significa quindi investire in imprese che compiono scelte aziendali sostenibili, coerenti con i principi del Global Compact delle Nazioni Unite, relativi a diritti umani, standard lavorativi, tutela dell'ambiente e lotta alla corruzione, gli obiettivi dell'Agenda 2030 delle Nazioni Unite per lo sviluppo sostenibile e dell'Accordo di Parigi sui cambiamenti climatici.







 Youtube
Youtube
 X - Banca d’Italia
X - Banca d’Italia
 Linkedin
Linkedin
 RSS
RSS